Comprehensive Guide to Shoulder Arthritis
Understanding Shoulder Arthritis: A Comprehensive Guide
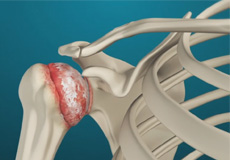
In the realm of joint ailments, shoulder arthritis stands as a prevalent condition that affects countless individuals worldwide. The gradual degeneration of the shoulder joint can lead to debilitating pain and restricted mobility. This extensive guide delves deep into the intricacies of shoulder arthritis, providing a holistic understanding of the condition, its causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures.
What Is Shoulder Arthritis?
Arthritis in the shoulder, also known as glenohumeral arthritis, is a condition characterized by the deterioration of the cartilage within the shoulder joint. The shoulder joint is a complex structure consisting of the humerus (upper arm bone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the clavicle (collarbone). These bones are held together by ligaments, tendons, and muscles, all of which work in harmony to facilitate smooth and pain-free movement.
Types of Shoulder Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis in the shoulder, with the following being the most common:
Osteoarthritis
- Also known as degenerative joint disease.
- The most common type of arthritis, often occurring in older people.
- Affects the cartilage, the tissue that cushions and protects the ends of bones in a joint.
- Causes joint pain and can limit a person’s normal range of motion.
- In severe cases, the shoulder joint may lose all movement, leading to disability.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- An autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks healthy joints, tissues, and organs.
- Often affects women of child-bearing age (15-44).
- Inflames the lining (or synovium) of joints, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of function.
- Can deform joints in severe cases.
- Typically affects joints symmetrically (both sides of the body).
Causes of Shoulder Arthritis
Understanding the root causes of arthritis in the shoulder is crucial in preventing its onset. Primary causes include:
- Aging: Natural degeneration of joint cartilage.
- Previous Injuries: Trauma or repetitive injuries to the shoulder can increase the risk.
- Genetics: A family history of arthritis can predispose individuals to the condition.
- Secondary Factors: Such as repeated trauma, surgery to the affected joint, or abnormal joint structures from birth.
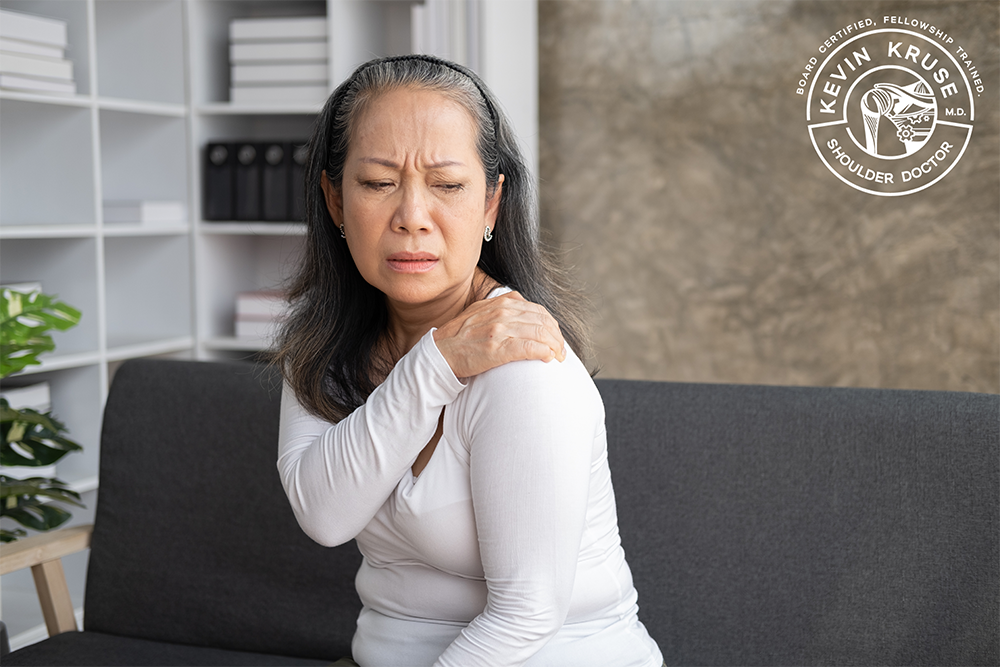
Arthritis of the Shoulder Symptoms
Symptoms of arthritis in the shoulder can vary but generally include:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the shoulder joint, especially during movement.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in moving the shoulder freely.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Limited ability to lift or rotate the arm.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling in the affected area.
- Morning Stiffness: Stiffness in the joints in the morning or after periods of inactivity.

Diagnosis and Evaluation
Doctors diagnose arthritis with a medical history, physical exam, and imaging studies like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans. These tools help in assessing the degree of cartilage damage and inflammation.
Treatment Options for this type of Arthritis
There is no cure for arthritis, but several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medicines, including NSAIDs, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve shoulder strength and mobility.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections for reducing pain and temporary relief.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical treatment may be recommended. Surgical options include:
- Shoulder Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to clean out the joint.
- Joint Debridement: Removal of damaged tissue from the joint.
- Shoulder Arthroplasty: Replacement of the damaged joint, either total or hemiarthroplasty.
Preventing Arthritis of the Shoulder
Prevention is always preferable to treatment. To reduce the risk of developing shoulder arthritis:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight places additional stress on joints.
- Exercise Regularly: Strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint.
- Avoid Overuse: Be mindful of repetitive shoulder movements.
Conclusion
Understanding shoulder arthritis is the first step in effectively managing and preventing this condition. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and adopting preventive measures can help maintain the health and function of your shoulder joint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is shoulder arthritis common in younger individuals?
Shoulder arthritis is more commonly seen in older adults, but it can affect individuals of all ages, especially if there is a history of injury or genetic predisposition.
Can I continue to exercise with shoulder arthritis?
Yes, low-impact exercises and physical therapy can help improve shoulder function and reduce pain in individuals with arthritis in the shoulder.
Are there any natural remedies for shoulder arthritis?
Some people find relief from natural remedies such as heat or cold therapy, dietary supplements, and herbal treatments, but these should be used in conjunction with medical advice.
What are the surgical options for this type of arthritis?
Surgical options may include shoulder arthroscopy, joint debridement, or shoulder joint replacement, depending on the severity of the condition.
How long does recovery take after shoulder joint replacement surgery?
Recovery time varies but may take several months. Physical therapy is typically recommended to aid in rehabilitation.
Contact Dallas shoulder surgeon Dr Kevin Kruse, who specializes in shoulder treatments for a consultation on improving your comfort and quality of life if you are afflicted with shoulder arthritis.
